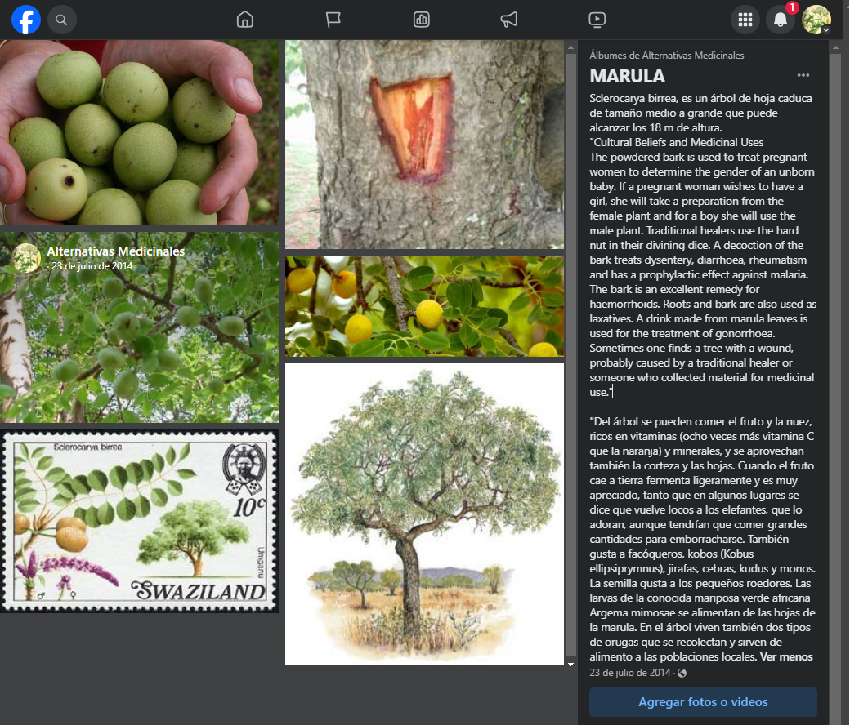
Sclerocarya birrea, es un árbol de hoja caduca de tamaño medio a grande que puede alcanzar los 18 m de altura.
"Cultural Beliefs and Medicinal Uses
The powdered bark is used to treat pregnant women to determine the gender of an unborn baby. If a pregnant woman wishes to have a girl, she will take a preparation from the female plant and for a boy she will use the male plant. Traditional healers use the hard nut in their divining dice. A decoction of the bark treats dysentery, diarrhoea, rheumatism and has a prophylactic effect against malaria. The bark is an excellent remedy for haemorrhoids. Roots and bark are also used as laxatives. A drink made from marula leaves is used for the treatment of gonorrhoea. Sometimes one finds a tree with a wound, probably caused by a traditional healer or someone who collected material for medicinal use."
"Del árbol se pueden comer el fruto y la nuez, ricos en vitaminas (ocho veces más vitamina C que la naranja) y minerales, y se aprovechan también la corteza y las hojas. Cuando el fruto cae a tierra fermenta ligeramente y es muy apreciado, tanto que en algunos lugares se dice que vuelve locos a los elefantes, que lo adoran, aunque tendrían que comer grandes cantidades para emborracharse. También gusta a facóqueros, kobos (Kobus ellipsiprymnus), jirafas, cebras, kudus y monos. La semilla gusta a los pequeños roedores. Las larvas de la conocida mariposa verde africana Argema mimosae se alimentan de las hojas de la marula. En el árbol viven también dos tipos de orugas que se recolectan y sirven de alimento a las poblaciones locales.
Marula
- Detalles
- Escrito por: Cata C Amaya
- Visto: 319